Understanding the types of ovarian cancer, recognizing my first symptoms of ovarian cancer, and knowing the available ovarian cancer treatment and ovarian cancer surgery options are crucial for early detection and improved survival rates.
This 2025 updated guide explores everything you need to know about ovarian cancer—from causes and risks to diagnosis, treatment, and future research directions.
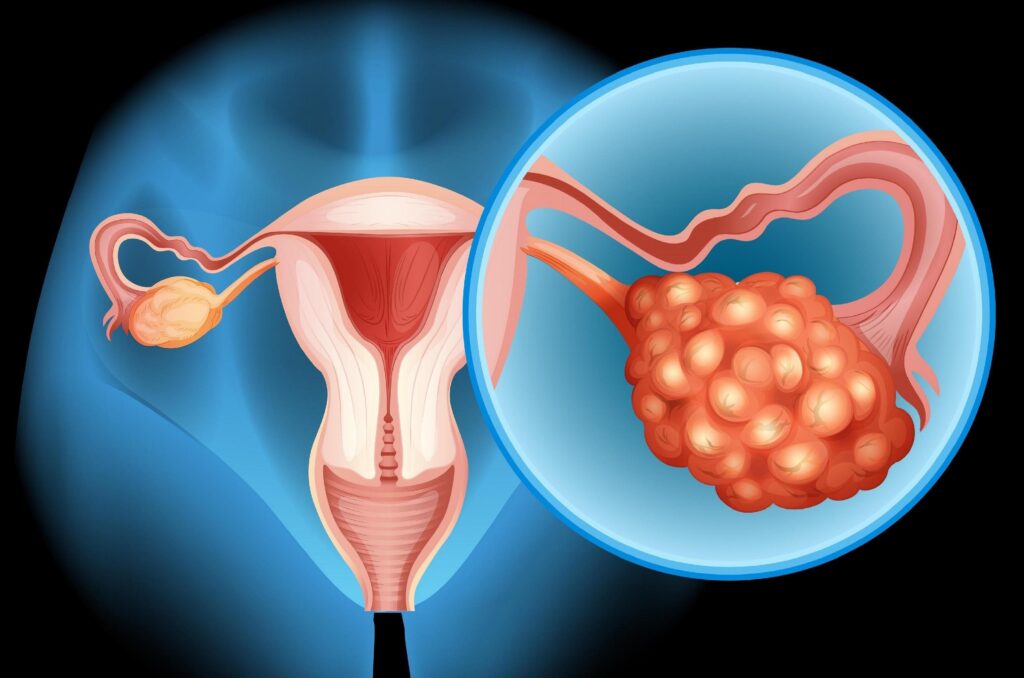
1. What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovaries, the female reproductive glands responsible for producing eggs and hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
It occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body.
2. My First Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
One of the challenges with ovarian cancer symptoms is that they are often subtle at first. Many women dismiss them as digestive issues, stress, or hormonal changes.
Common Early Symptoms:
-
Persistent bloating or swelling in the abdomen
-
Pelvic or abdominal pain
-
Feeling full quickly while eating
-
Urgent or frequent urination
Other Possible Symptoms:
-
Fatigue
-
Indigestion
-
Back pain
-
Menstrual irregularities
Many survivors report that “my first symptoms of ovarian cancer” were persistent bloating or unusual pelvic discomfort, which they initially ignored.
3. Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing ovarian cancer, including:
-
Age: Most common in women over 50.
-
Family History: BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic mutations raise risk.
-
Reproductive History: Never having been pregnant or late pregnancy.
-
Hormonal Factors: Prolonged hormone replacement therapy.
-
Lifestyle: Obesity, poor diet, smoking.
4. Types of Ovarian Cancer
There are several types of ovarian cancer, classified based on where the cancer begins:
-
Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
-
Most common (90% of cases).
-
Starts in the thin tissue covering the ovaries.
-
-
Germ Cell Tumors
-
Rare, but more likely in younger women.
-
Originate from egg-producing cells.
-
-
Stromal Tumors
-
Begin in hormone-producing cells.
-
Often detected earlier due to hormone-related symptoms.
-
-
Borderline Tumors
-
Slow-growing, less aggressive, but still need monitoring.
-
Understanding the types of ovarian cancer helps doctors tailor treatments more effectively.
5. Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer
Because ovarian cancer symptoms mimic other conditions, diagnosis can be challenging. Doctors use:
-
Pelvic Examination – to feel abnormalities in the ovaries.
-
Ultrasound/CT/MRI scans – for detailed imaging.
-
CA-125 Blood Test – measures a protein often elevated in ovarian cancer.
-
Biopsy – definitive confirmation by examining tumor tissue.
Early detection significantly increases survival chances.
6. Ovarian Cancer Treatment Options (2025)
Ovarian cancer treatment depends on stage, type, and patient health.
a) Surgery
Ovarian cancer surgery is often the first step, aiming to remove as much of the tumor as possible. Depending on the stage, this may include:
-
Removal of one or both ovaries.
-
Hysterectomy (removal of the uterus).
-
Removal of nearby lymph nodes or affected tissues.
b) Chemotherapy
Often used after surgery to kill remaining cancer cells. Drugs like paclitaxel and carboplatin remain standard choices.
c) Targeted Therapy
Medications designed to attack specific cancer genes or proteins, such as PARP inhibitors for BRCA-mutated cancers.
d) Immunotherapy
An evolving ovarian cancer treatment option, helping the immune system identify and destroy cancer cells.
e) Hormone Therapy
Used in some types of ovarian cancer that are hormone-sensitive.
7. Advances in Ovarian Cancer Surgery
Modern surgical approaches are becoming less invasive and more precise:
-
Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive, shorter recovery.
-
Cytoreductive Surgery: Removes visible tumor tissue to maximize chemotherapy effectiveness.
-
Fertility-Sparing Surgery: For younger women, allows preservation of reproductive ability in early stages.
8. Life After Ovarian Cancer Treatment
Survivorship is a critical phase. Many women wonder what to expect after ovarian cancer treatment.
-
Follow-up Care: Regular blood tests, scans, and exams.
-
Emotional Support: Counseling and support groups help cope with anxiety and fear of recurrence.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments: Healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management boost recovery.
9. Prognosis and Survival Rates
Survival rates depend on cancer stage and type.
-
Early Stage (I–II): 70–90% 5-year survival rate.
-
Advanced Stage (III–IV): Drops to around 20–40%.
This highlights the importance of recognizing ovarian cancer symptoms early and not ignoring persistent abdominal or pelvic issues.
10. Future of Ovarian Cancer Research (2025 and Beyond)
The future looks more promising with advancements in:
-
Genomic Testing: Personalized therapies based on genetic profiles.
-
New Targeted Drugs: Focused on blocking cancer cell repair mechanisms.
-
Immunotherapy Trials: Combining immune-based treatments with chemotherapy.
These innovations aim to make ovarian cancer treatment more effective, with fewer side effects and higher survival chances.
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer is a challenging disease, but awareness of ovarian cancer symptoms, timely detection, and advanced medical treatments can save lives.
From understanding the types of ovarian cancer to recognizing my first symptoms of ovarian cancer, women can take proactive steps in protecting their health. Advances in ovarian cancer treatment and ovarian cancer surgery continue to bring new hope for patients and families around the world.
The key is awareness: listening to your body, seeking medical advice early, and staying informed about the latest research.
References
-
American Cancer Society – Ovarian Cancer
👉 https://www.cancer.org/cancer/ovarian-cancer.html -
National Cancer Institute – Ovarian Cancer Treatment (PDQ)
👉 https://www.cancer.gov/types/ovarian/patient/ovarian-treatment-pdq -
Mayo Clinic – Ovarian Cancer Symptoms & Causes
👉 https://www.mayoclinic.org -
National Ovarian Cancer Coalition – Ovarian Cancer Overview
👉 https://ovarian.org -
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology – Advances in Ovarian Cancer Therapy (2024)
👉 https://www.nature.com/nrclinonc
